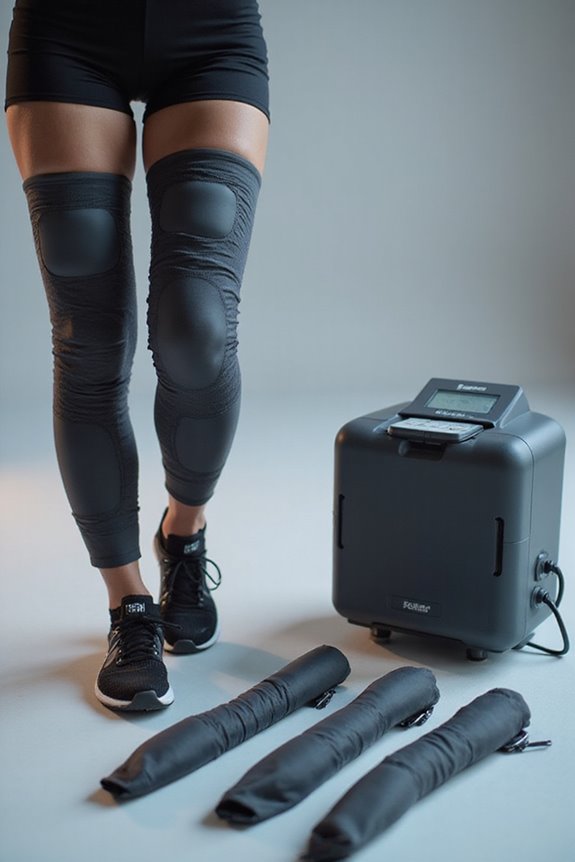
Pneumatic compression devices (PCDs) provide several advantages:
- Clinical Effectiveness: They reduce venous thromboembolism (VTE) incidence, especially post-surgery, and are effective for patients who cannot take anticoagulants.
- Quality of Life: PCDs enhance mobility, decrease swelling by up to 28%, and improve psychological well-being.
- Economic Benefits: They lower healthcare costs by 69% annually and reduce hospitalizations by 59%.
- Infection Control: PCDs improve circulation and reduce infection rates.
Further details are available below.
Key Takeaways
- Pneumatic compression devices (PCDs) significantly reduce venous thromboembolism (VTE) incidence, particularly in post-surgical patients.
- They enhance quality of life by improving mobility, reducing limb swelling, and boosting psychological well-being.
- PCDs lower healthcare costs by reducing hospitalizations and outpatient treatment expenses, making them economically beneficial.
- They improve infection control by enhancing circulation and immune function, thereby reducing secondary infections in at-risk patients.
- PCDs are effective alternatives to anticoagulants for patients unable to take medication, promoting consistent prophylaxis.
Clinical Effectiveness
The clinical effectiveness of pneumatic compression devices (PCDs) is well-documented across various medical applications. These devices play a vital role in the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE), especially among hospitalized patients.
- Intermittent pneumatic compression devices (IPCDs) markedly decrease VTE incidence, particularly in post-surgical cases.
- Recommended as a prophylactic measure for patients unable to take anticoagulants, IPCDs present a lower bleeding risk.
- Clinical guidelines endorse IPC use in conjunction with other protocols to enhance patient outcomes.
Proper adherence to treatment protocols is essential; patient education and monitoring can optimize the effectiveness of IPCDs. Comparative studies indicate that IPCDs may demonstrate similar or superior efficacy to certain pharmacological options, reinforcing their clinical utility in targeted patient populations.
Quality of Life Improvements
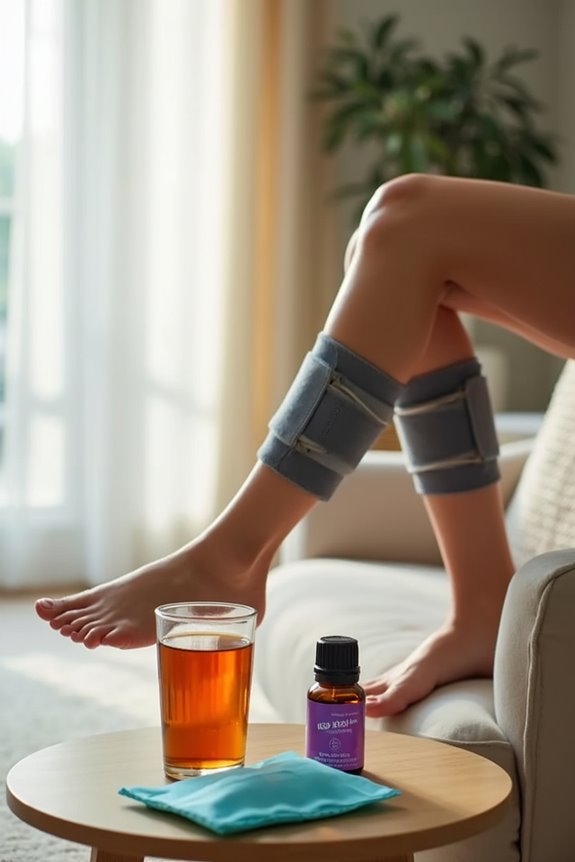

Quality of life improvements associated with pneumatic compression devices (PCDs) are significant, particularly for patients managing chronic lymphedema.
- Enhanced physical comfort is achieved through reduced limb swelling, with patients reporting volume decreases up to 28%.
- This reduction contributes to improved mobility and functional status, allowing greater participation in daily activities and social engagement.
- The psychological impact is notable; alleviating symptoms reduces anxiety and enhances self-image, fostering emotional resilience.
- Patients experience increased autonomy, decreasing family and caregiver burdens.
- As individuals regain confidence, they engage more in recreational activities and social interactions, promoting overall well-being.
- The combination of these factors leads to higher patient satisfaction and a more fulfilling lifestyle, aligning with the desire for belonging within social contexts.
Economic Benefits

Economic benefits associated with pneumatic compression devices (PCDs) are substantial, as they greatly reduce healthcare costs while improving patient outcomes.
- Cost Savings: Advanced pneumatic compression devices (APCDs) can lower annual healthcare costs by 69% per patient compared to conventional devices, reducing costs from $12,253 to $3,839.
- Healthcare Efficiency: APCDs result in 59% fewer hospitalizations, leading to 82% and 55% reductions in inpatient and outpatient costs, respectively.
- Outpatient and Therapy Costs: Outpatient treatment expenses decrease by 55-85%, while physical therapy visits drop by 30-34%.
- Complication Rates: APCDs reduce cellulitis incidence by 75-79%, considerably lowering costs associated with infections and hospital admissions.
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention
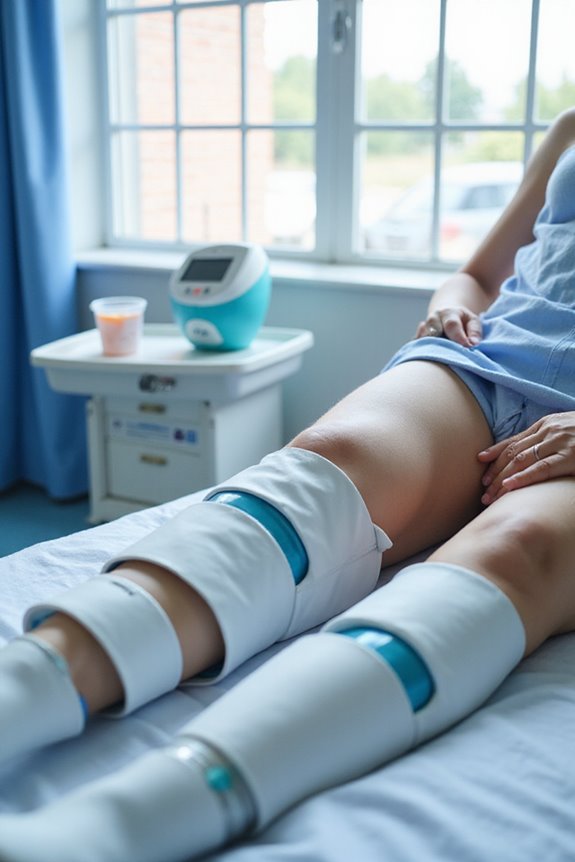
Pneumatic compression devices (PCDs) play a significant role in preventing venous thromboembolism (VTE), a serious condition that can arise in various patient populations. These devices reduce venous stasis, enhancing blood flow and promoting fibrinolysis, which aids in clot breakdown. By simulating leg movements through mechanical stimulation, PCDs effectively maintain circulation, especially during surgical procedures.
Key benefits include:
- Comparable VTE risk reduction to anticoagulation therapy, particularly for surgical patients.
- Efficacy in low to moderate-risk groups, evidenced by a mere 0.18% VTE incidence in elective spine surgery patients.
- Enhanced patient compliance due to ease of use, contributing to consistent prophylaxis.
PCDs provide a crucial complementary option to pharmacological methods, especially when anticoagulants are contraindicated.
Infection Control
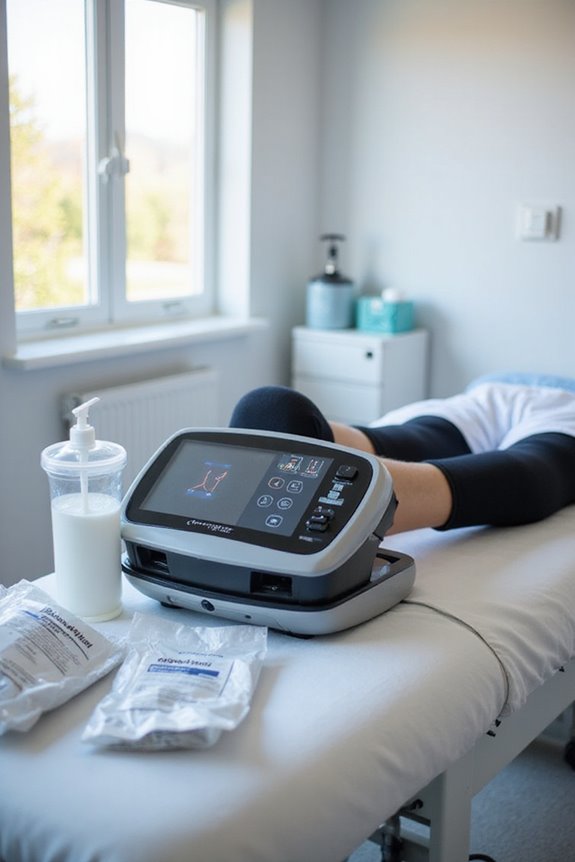
Infection control is a critical consideration in healthcare settings, particularly for patients with compromised lymphatic systems or those who are immobile. Pneumatic compression devices play an essential role in infection prevention by:
- Reducing infection rates in lymphedema patients through improved lymphatic drainage, which decreases stagnant fluid.
- Enhancing immune function via increased circulation, facilitating immune cell transport and pathogen clearance.
- Preventing secondary infections in immobile or post-surgical patients by maintaining circulation and minimizing skin breakdown.
- Supporting edema management, which mitigates infection risk by improving skin barrier function and reducing microfissures.
- Complementing existing infection control protocols, thereby lowering dependence on antibiotics and enhancing overall clinical outcomes.
These mechanisms collectively contribute to sustained immune enhancement and a significant reduction in infection incidence among vulnerable populations.
Functional and Practical Benefits
The benefits of pneumatic compression devices extend beyond infection control, offering significant functional and practical advantages for patients.
Enhanced Circulation and Recovery
- These devices promote enhanced blood flow, reducing the risk of clot formation.
- They support lymphatic drainage, decreasing swelling and promoting fluid balance, which aids muscle recovery.
User Comfort and Convenience****
- Pneumatic compression is a drug-free alternative, vital for patients unable to take anticoagulants.
- The portability of the devices allows for ease of use in various settings, enhancing patient adherence.
Quality of Life Improvements
- Studies indicate improvements in functional status and independence, particularly for those with mobility impairments.
- Reduced swelling and discomfort translate to better performance in daily activities, fostering overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Pneumatic Compression Devices Work Mechanically?
Pneumatic compression devices operate through mechanical pressure cycles, inflating and deflating to enhance circulation. This rhythmic action mimics natural muscle movements, promoting blood flow and fostering a sense of community well-being among users seeking health improvement.
Are There Any Contraindications for Using These Devices?
Contraindications for using pneumatic compression devices span several categories, including severe cardiovascular issues, infections, and anatomical limitations. Prioritizing patient safety is essential, as improper use may lead to serious health complications or exacerbate existing conditions.
Can These Devices Be Used During Pregnancy?
Like a lifeline in turbulent waters, pneumatic compression devices can be safely used during pregnancy. Addressing pregnancy concerns, they enhance venous return while ensuring pneumatic safety, making them a valuable option for at-risk women.
How Long Should I Wear a Pneumatic Compression Device Each Day?
Experts recommend a wearing schedule of at least 18 to 20 hours daily for pneumatic compression devices. Adhering to this daily duration maximizes therapeutic effects, particularly for those at risk of venous complications.
Are There Any Side Effects Associated With Pneumatic Compression Therapy?
“Curiosity killed the cat,” yet understanding therapy risks is essential. Pneumatic compression therapy can lead to side effects like skin irritation, discomfort, and rare complications, necessitating careful monitoring and appropriate device fitting for effective use.